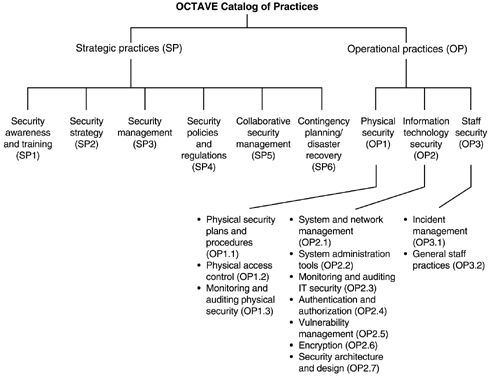
Appendix C. Catalog of PracticesThis document contains the catalog of practices used in the OCTAVE approach. The catalog of practices comprises a collection of good strategic and operational security practices. An organization that is conducting an information security risk evaluation measures itself against this catalog of practices. The catalog is used as a measurement for what the organization is currently doing well with respect to security (its current security practices) and what it is not doing well (its organizational vulnerabilities). During each knowledge elicitation workshop, participants fill out a survey and then discuss any issues from the survey that they feel are important. The catalog of practices is also used during the creation of a new or revised protection strategy for the organization and risk mitigation plans.
The catalog of practices is deliberately divided into two types of practices: strategic and operational. Strategic practices focus on organizational issues at the policy level and provide good general management practices. Strategic practices include issues that are business-related as well as those that require organizationwide planning and participation. Operational practices focus on technology-related concerns. They include issues related to how people use, interact with, and protect technology. Since strategic practices are based on good management practice, they should be fairly stable over time. Operational practices are more subject to changes as technology advances and new practices arise to deal with those changes.
The catalog of practices is a general catalog; it is not specific to any domain, organization, or set of regulations. It can be modified to suit a particular domain's standard of due care or set of regulations (e.g., the medical community and HIPPA security regulations). It can also be extended to add organization-specific standards, or it can be modified to reflect the terminology of a specific domain.
Figure C-1 depicts the structure of the catalog of practices; the details can be found on the following pages. This catalog was developed using several sources, which are referenced on the last page of this appendix. In addition to these security-related references, we also used our experience developing, delivering, and analyzing the results of the Information Security Evaluation (ISE), a vulnerability assessment technique developed by the Software Engineering Institute and delivered to a variety of organization over the past six years.
| SP1.1 |
Staff members understand their security roles and responsibilities. This is documented and verified. |
| SP1.2 |
There is adequate in-house expertise for all supported services, mechanisms, and technologies (e.g., logging, monitoring, or encryption), including their secure operation. This is documented and verified. |
| SP1.3 |
Security awareness, training, and periodic reminders are provided for all personnel. Staff understanding is documented and conformance is periodically verified. Training includes these topics:
Security strategies, goals, and objectives Security regulations, policies, and procedures Policies and procedures for working with third parties Contingency and disaster recovery plans Physical security requirements Users' perspective on
- system and network management - system administration tools - monitoring and auditing for physical and information technology security - authentication and authorization - vulnerability management - encryption - architecture and design Incident management General staff practices Enforcement, sanctions, and disciplinary actions for security violations How to properly access sensitive information or work in areas where sensitive information is accessible Termination policies and procedures relative to security |
| SP2.1 |
The organization's business strategies routinely incorporate security considerations. |
| SP2.2 |
Security strategies and policies take into consideration the organization's business strategies and goals. |
| SP2.3 |
Security strategies, goals, and objectives are documented and are routinely reviewed, updated, and communicated to the organization. |
| SP3.1 |
Management allocates sufficient funds and resources to information security activities. |
| SP3.2 |
Security roles and responsibilities are defined for all staff in the organization. |
| SP3.3 |
The organization's hiring and termination practices for staff take information security issues into account. |
| SP3.4 |
The required levels of information security and how they are applied to individuals and groups are documented and enforced. |
| SP3.5 |
The organization manages information security risks, including
Assessing risks to information security both periodically and in response to major changes in technology, internal/external threats, or the organization's systems and operations Taking steps to mitigate risks to an acceptable level Maintaining an acceptable level of risk Using information security risk assessments to help select cost-effective security/control measures, balancing implementation costs against potential losses |
| SP3.6 |
Management receives and acts upon routine reports summarizing the results of
Review of system logs Review of audit trails Technology vulnerability assessments Security incidents and the responses to them Risk assessments Physical security reviews Security improvement plans and recommendations |
| SP4.1 |
The organization has a comprehensive set of documented, current policies that are periodically reviewed and updated. These policies address key security topic areas, including
Security strategy and management Security risk management Physical security System and network management System administration tools Monitoring and auditing Authentication and authorization Vulnerability management Encryption Security architecture and design Incident management Staff security practices Applicable laws and regulations Awareness and training Collaborative information security Contingency planning and disaster recovery |
| SP4.2 |
There is a documented process for management of security policies, including
|
| SP4.3 |
The organization has a documented process for periodic evaluation (technical and nontechnical) of compliance with information security policies, applicable laws and regulations, and insurance requirements. |
| SP4.4 |
The organization has a documented process to ensure compliance with information security policies, applicable laws and regulations, and insurance requirements. |
| SP4.5 |
The organization uniformly enforces its security policies. |
| SP4.6 |
Testing and revision of security policies and procedures are restricted to authorized personnel. |
| SP5.1 |
The organization has documented, monitored, and enforced procedures for protecting its information when working with external organizations (e.g., third parties, collaborators, subcontractors, or partners). |
| SP5.2 |
The organization has verified that outsourced security services, mechanisms, and technologies meet its needs and requirements. |
| SP5.3 |
The organization documents, monitors, and enforces protection strategies for information belonging to external organizations that is accessed from its own infrastructure components or is used by its own personnel. |
| SP5.4 |
The organization provides and verifies awareness and training on applicable external organizations' security policies and procedures for personnel who are involved with those external organizations. |
| SP5.5 |
There are documented procedures for terminated external personnel specifying appropriate security measures for ending their access. These procedures are communicated and coordinated with the external organization. |
| SP6.1 |
An analysis of operations, applications, and data criticality has been performed. |
| SP6.2 |
The organization has documented
Business continuity or emergency operation plans Disaster recovery plan(s) Contingency plan(s) for responding to emergencies |
| SP6.3 |
The contingency, disaster recovery, and business continuity plans consider physical and electronic access requirements and controls. |
| SP6.4 |
The contingency, disaster recovery, and business continuity plans are periodically reviewed, tested, and revised. |
| SP6.5 |
All staff
Are aware of the contingency, disaster recovery, and business continuity plans Understand and are able to carry out their responsibilities |
| OP1.1.1 |
There are documented facility security plan(s) for safeguarding the premises, buildings, and any restricted areas. |
| OP1.1.2 |
These plans are periodically reviewed, tested, and updated. |
| OP1.1.3 |
Physical security procedures and mechanisms are routinely tested and revised. |
| OP1.1.4 |
There are documented policies and procedures for managing visitors, including
Sign in Escort Access logs Reception and hosting |
| OP1.1.5 |
There are documented policies and procedures for physical control of hardware and software, including
Workstations, laptops, modems, wireless components, and all other components used to access information Access, storage, and retrieval of data backups Storage of sensitive information on physical and electronic media Disposal of sensitive information or the media on which it is stored Reuse and recycling of paper and electronic media |
| OP1.2.1 |
There are documented policies and procedures for individual and group access covering
The rules for granting the appropriate level of physical access The rules for setting an initial right of access Modifying the right of access Terminating the right of access Periodically reviewing and verifying the rights of access |
| OP1.2.2 |
There are documented policies, procedures, and mechanisms for controlling physical access to defined entities. This includes
|
| OP1.2.3 |
There are documented procedures for verifying access authorization prior to granting physical access. |
| OP1.2.4 |
Workstations and other components that allow access to sensitive information are physically safeguarded to prevent unauthorized access. |
| OP1.3.1 |
Maintenance records are kept to document the repairs and modifications of a facility's physical components. |
| OP1.3.2 |
An individual's or group's actions, with respect to all physically controlled media, can be accounted for. |
| OP1.3.3 |
Audit and monitoring records are routinely examined for anomalies, and corrective action is taken as needed. |
| OP2.1.1 |
There are documented security plan(s) for safeguarding the systems and networks. |
| OP2.1.2 |
Security plan(s) are periodically reviewed, tested, and updated. |
| OP2.1.3 |
Sensitive information is protected by secure storage, such as
|
| OP2.1.4 |
The integrity of installed software is regularly verified. |
| OP2.1.5 |
All systems are up to date with respect to revisions, patches, and recommendations in security advisories. |
| OP2.1.6 |
There is a documented data backup plan that
|
| OP2.1.7 |
All staff understand and are able to carry out their responsibilities under the backup plans. |
| OP2.1.8 |
Changes to IT hardware and software are planned, controlled, and documented. |
| OP2.1.9 |
IT staff members follow procedures when issuing, changing, and terminating users' passwords, accounts, and privileges.
Unique user identification is required for all information system users, including third-party users. Default accounts and default passwords have been removed from systems. |
| OP2.1.10 |
Only necessary services are running on systems; all unnecessary services have been removed. |
| OP2.2.1 |
New security tools, procedures, and mechanisms are routinely reviewed for applicability in meeting the organization's security strategies. |
| OP2.2.2 |
Tools and mechanisms for secure system and network administration are used, and are routinely reviewed and updated or replaced. Examples are
Data integrity checkers Cryptographic tools Vulnerability scanners Password quality-checking tools Virus scanners Process management tools Intrusion detection systems Secure remote administrations Network service tools Traffic analyzers Incident response tools Forensic tools for data analysis |
| OP2.3.1 |
System and network monitoring and auditing tools are routinely used by the organization.
Activity is monitored by the IT staff. System and network activity is logged/recorded. Logs are reviewed on a regular basis. Unusual activity is dealt with according to the appropriate policy or procedure. Tools are periodically reviewed and updated. |
| OP2.3.2 |
Firewall and other security components are periodically audited for compliance with policy. |
| OP2.4.1 |
Appropriate access controls and user authentication (e.g., file permissions, network configuration) consistent with policy are used to restrict user access to
Information Systems utilities Program source code Sensitive systems Specific applications and services Network connections within the organization Network connections from outside the organization |
| OP2.4.2 |
There are documented information-use policies and procedures for individual and group access to
Establish the rules for granting the appropriate level of access Establish an initial right of access Modify the right of access Terminate the right of access Periodically review and verify the rights of access |
| OP2.4.3 |
Access control methods/mechanisms restrict access to resources according to the access rights determined by policies and procedures. |
| OP2.4.4 |
Access control methods/mechanisms are periodically reviewed and verified. |
| OP2.4.5 |
Methods or mechanisms are provided to ensure that sensitive information has not been accessed, altered, or destroyed in an unauthorized manner. |
| OP2.4.6 |
Authentication mechanisms are used to protect availability, integrity, and confidentiality of sensitive information. Examples are
Digital signatures Biometrics |
| OP2.5.1 |
There is a documented set of procedures for managing vulnerabilities, including
Selecting vulnerability evaluation tools, checklists, and scripts Keeping up to date with known vulnerability types and attack methods Reviewing sources of information on vulnerability announcements, security alerts, and notices Identifying infrastructure components to be evaluated Scheduling of vulnerability evaluations Interpreting and responding to the results Maintaining secure storage and disposition of vulnerability data |
| OP2.5.2 |
Vulnerability management procedures are followed and are periodically reviewed and updated. |
| OP2.5.3 |
Technology vulnerability assessments are performed on a periodic basis, and vulnerabilities are addressed when they are identified. |
| OP2.6.1 |
Appropriate security controls are used to protect sensitive information while in storage and during transmission, including
Data encryption during transmission Data encryption when writing to disk Use of public key infrastructure Virtual private network technology Encryption for all Internet-based transmission |
| OP2.6.2 |
Encrypted protocols are used when remotely managing systems, routers, and firewalls. |
| OP2.6.3 |
Encryption controls and protocols are routinely reviewed, verified, and revised. |
| OP2.7.1 |
System architecture and design for new and revised systems include considerations for
Security strategies, policies, and procedures History of security compromises Results of security risk assessments |
| OP2.7.2 |
The organization has up-to-date diagrams that show the enterprisewide security architecture and network topology. |
| OP3.1.1 |
Documented procedures exist for identifying, reporting, and responding to suspected security incidents and violations, including
|
| OP3.1.2 |
Incident management procedures are periodically tested, verified, and updated. |
| OP3.1.3 |
There are documented policies and procedures for working with law enforcement agencies. |
| OP3.2.1 |
Staff members follow good security practice, such as
Securing information for which they are responsible Not divulging sensitive information to others (resistance to social engineering) Having adequate ability to use information technology hardware and software Using good password practices Understanding and following security policies and regulations Recognizing and reporting incidents |
| OP3.2.2 |
All staff at all levels of responsibility implement their assigned roles and responsibility for information security. |
| OP3.2.3 |
There are documented procedures for authorizing and overseeing those who work with sensitive information or who work in locations where the information resides. This includes
Employees Contractors, partners, collaborators, and personnel from third-party organizations Systems maintenance personnel Facilities maintenance personnel |
|